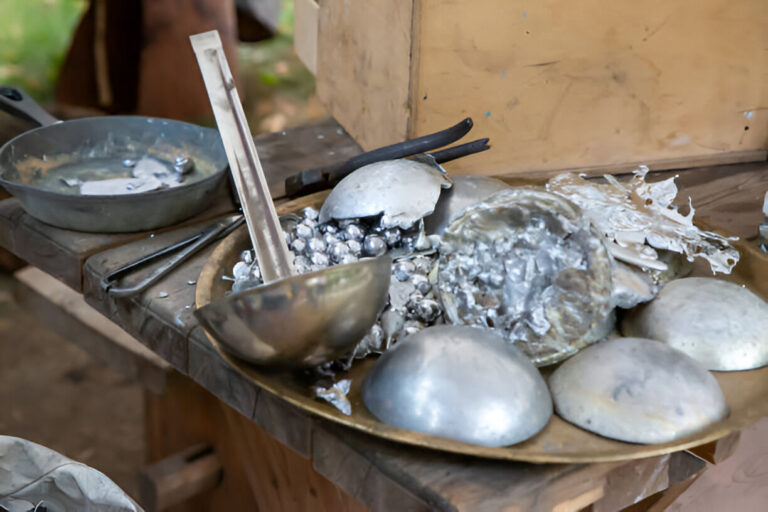
Basics of Zinc Die Casting
Zinc die casting involves specific alloys and the hot chamber casting technique. Both how these alloys work and the manufacturing rules they follow are key to making closely detailed and strong parts.
Understanding Zinc Alloys
Zinc alloys are essential in die casting because of their unique properties. High dimensional accuracy and resistance to corrosion make these alloys a popular choice in manufacturing. The density of zinc affects the weight and cost of products, making them ideal for making small parts. Zinc’s melting point ranges from 387°C to 390°C for alloys, which allows for efficient casting.
These alloys, while not being super light, help create items with strong resistance to wear. Designers consider factors like strength and flexibility as they choose the right alloy. This ensures that products not only meet functional needs, but also fit industry standards.
Die Casting Process and Techniques
The die casting process uses a hot chamber technique to create the desired shapes. First, the die mold is prepared and cleaned from impurities. Then, melted zinc is poured into this mold. This process creates complex shapes while keeping high precision in the details.
Various techniques are used to enhance production based on part sizes and machine types. Key benefits include high production volumes and low production costs. Zinc die casting allows you to make parts with fine details, maintaining excellent surface finish and good strength. The process is favored for its speed and efficiency, providing consistent results in large batches.
Properties and Advantages
Zinc casting offers unique benefits that make it attractive in many industries. It provides a blend of strength, adaptability, and aesthetic possibilities. This section focuses on the physical and mechanical characteristics, as well as the advantages of selecting zinc for casting processes.
Physical and Mechanical Characteristics
Zinc alloys stand out due to their strength and durability. With impressive tensile strength and impact resistance, zinc can handle the stress and strain that come with various applications. This makes it a robust choice for creating parts that need to withstand wear and tear.
Corrosion resistance is another key property of zinc alloys. This makes zinc die casting suitable for applications in environments where rust could be a problem. The low melting point of zinc offers energy efficiency during casting. It allows for the creation of intricate shapes with fine details, which is a significant advantage for designers and engineers.
However, zinc is dense, which means it is mostly used for smaller parts. Its dimensional stability ensures parts retain their shape under different conditions, reducing the risk of warping.
Why Choose Zinc for Casting
Opting for zinc die casting brings several advantages that you might find beneficial. One notable advantage is the excellent surface finish zinc offers. Die-cast zinc parts can be finished to a high polish or tailored with different textures to meet specific visual needs.
Besides aesthetics, zinc also provides superior strength and durability without the weight typically associated with other metals. This makes it a practical option for industries such as automotive, electronics, and consumer goods, where both performance and appearance matter.
Moreover, the environmental impact of zinc manufacturing is minimized, as it produces less pollution and greenhouse gases. These benefits make zinc casting a favored choice for businesses looking to produce high-quality, sustainable products.
Design and Manufacturing
In the world of zinc casting, creating complex shapes while maintaining precision and quality is essential. The process allows for tight tolerances and dimensional accuracy, which are key factors when striving for excellence in manufacturing.
Creating Complex Geometries
Zinc casting excels at making complex shapes with intricate details. You can achieve stunning geometries that are often impossible with other methods. Thanks to the malleability of zinc alloys, it becomes easier to produce parts with unique forms.
Using these materials, you can create detailed designs with smooth surfaces. This process supports creativity and innovation in product design, enabling the development of new products with reliable performance.
Precision and Quality Control
Precision is at the heart of zinc casting, which is known for producing components with tight tolerances. This precision ensures that your parts fit perfectly in their intended applications, enhancing functionality and durability.
Quality control is crucial for maintaining high standards. Each stage of production uses techniques like inspection and testing to confirm dimensional accuracy. By monitoring these steps closely, you help guarantee that the final product meets both your expectations and industry standards.
Common Applications of Zinc Casting Parts
Zinc casting parts are widely used due to their excellent strength, durability, and ability to form complex shapes. You’ll often find them employed in the automotive sector and incorporated into various electronic and consumer products.
In the Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, zinc casting parts play a crucial role. They are often used to create components like transmission housings and engine blocks due to their strength and precision. Zinc allows for intricate designs while maintaining cost-effectiveness.
Another reason zinc is favored in cars is its ability to resist corrosion. This makes zinc ideal for parts exposed to challenging environmental conditions, like suspension systems and door handles. You’ll appreciate how zinc parts contribute to making vehicles safer and more reliable.
Zinc in Electronics and Consumer Goods
Zinc casting parts are also valuable in electronics and consumer goods. They offer flexibility in creating detailed components such as connectors and heat sinks. These parts need to be precise to ensure electronics function correctly, and zinc is up to the task.
In consumer goods, zinc’s aesthetics and strength make it perfect for items like kitchen appliances and decorative hardware. Its ability to take on various finishes improves the look and longevity of these products. You’ll find zinc casting adds both value and appeal to everyday items.
Comparison with Other Metals
Zinc die casting offers unique advantages over alternative metals like aluminum, magnesium, and copper. When deciding which metal to use, you should consider properties like density, corrosion resistance, and melting point. This choice affects factors like durability, cost, and ease of manufacturing.
Zinc vs. Aluminum and Magnesium
Zinc is denser than both aluminum and magnesium, giving it a sturdier feel. The density of zinc is about 7.1 g/cm³, making it much heavier compared to aluminum’s 2.7 g/cm³ and magnesium’s 1.7 g/cm³. This extra weight can add to the durability and toughness of zinc parts.
Zinc melts at a lower temperature of 419°C (787°F), allowing for less energy consumption in casting. Aluminum and magnesium require more energy due to their higher melting points, 660°C (1220°F) and 650°C (1202°F), respectively.
Zinc also shines in corrosion resistance. When exposed to harsh environments, zinc parts last longer compared to aluminum and magnesium, which need extra coatings for protection. This quality can be crucial for parts exposed to moisture and chemicals, saving you time and money on maintenance.
Zinc Alloy Variants & Comparisons
Different zinc alloys offer varying strengths and wear resistance, which make them adaptable to specific needs. For example, zinc-aluminum (ZA) alloys are known for higher strength and ease of machining, perfect for parts needing added durability under pressure.
Compared to copper alloys, zinc alloys are more cost-effective and easier to work with due to their lower melting points. While copper offers excellent electrical conductivity, it requires higher temperatures and costs more to process.
If you seek fine details and complex shapes in your parts, zinc alloys provide great flexibility. Their capacity for intricate designs often surpasses that of other metals, letting you create precise, detailed components.
Post-Processing and Finishing
In zinc casting, the final touches play a crucial role in enhancing both the appearance and functionality of parts. Post-processing not only involves improving the surface finish but also ensures environmentally friendly practices by reducing material waste.
Surface Treatment Options
When it comes to the surface finish of zinc die-cast parts, there are several ways to achieve the desired result. Painting and powder coating are two popular choices that can add color while providing a protective layer.
For a more natural look, polishing can be used to enhance the surface luster. Another method is electroplating, which involves coating the surface with metal to increase durability and resistance to corrosion. Each treatment offers different benefits, giving you the flexibility to choose what works best for your needs.
Reducing Material Waste
Decreasing material waste is an essential part of the zinc casting process. Using advanced trimming techniques, excess material can be removed efficiently, cutting down on waste.
Recent innovations focus on recycling the surplus zinc from casting operations. This helps in minimizing waste and making production more environmentally friendly. Efficient design practices are also crucial, as they help in optimizing the amount of material used in the first place, leading to less waste overall. Taking these steps not only benefits the environment but can also help reduce costs.